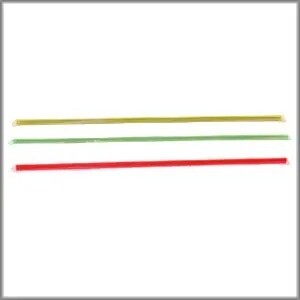
Brazos Lightning Rod Fibre Optic 3pk Red, Green, Yellow
This is the brightest fiber optic on the market. A veritable beacon of light available in 12-inch lengths of red, green, and yellow fiber optic rod.To produce a smaller, yet brilliant dot, the Brazos Custom Lightning Rod MiniDot and MicroDot Fiber Optic Sights use the thinner 0.040″ diameter fiber optic rod. The thicker 0.060″ diameter fiber optic rod is used in the BCG Lightning Rod standard fiber optic sights as well as by some manufacturers. Measure to be sure.
It’s not just a piece of plastic, rather a scientific component designed to capture, flouresce, and emit light through a precise orb. This true fiber optic is composed of a core layer of material impregnated with a flourescing compound that reacts to ultraviolet (UV) light. It is surrounded by a thin sheathing layer with a refraction index different from the core. UV light enters through the sides of the fiber where it is trapped due to the differing refraction indices of the sheath and core. The UV light causes material in the core to flouresce and project visible light out the end of the tube. Hence, the longer the tube, the more light is captured and projected out the end. And even on a cloudy day, there is still lots of UV light available to fire up the fiber optic.